
I C≈ I E How Emitter Resistor, R E, Fights Against the Instability of β The collector current I C is approximately equal to the emitter current. Then, we calculate for the emitter current using the following formula: We calculate R B below, which we will use the next calculation for I E. The base supply voltage, V BB, is calculated by: One resistor, the emitter resistor, R EĪlso helps provide stability against variations in β that may exist from transistor to transistor.īelow is a typical BJT receiving voltage divider bias:įor the circuit above, we're going to assume that β=100 for the transistor. That voltage is divided and distributed into the transistor at correct levels. Voltage divider bias is the most popular and used way to bias a transistor. Provide more stability against the changes that may exist in β of a transistor.Īnother way to bias a transistor is by voltage divider bias. We will explore other methods of transistor biasing including voltage-divider bias and emitter-supply bias, which Therefore, transistors are not commonly biased in this way. Base bias, then,Ĭan produce erratic circuit behavior due to transistor variations.

Is also susceptible to changes due to temperature, as it can vary pretty largely due to ambient temperature. Therefore, base bias can lead to unpredictableĪctions if a transistor needs to be replaced and there are variations in the β dc of that transistor. β dcĬan vary largely across transistors even of the same exact model and type. Β dc of a transistor is one of the most unstable and unpredictable parameters of a transistor. This is because the collector current, I C, is decided by purely by the β dc of the transistor. Though base bias is one of the simplest and easiest methods to bias transistors, it is the least popular way to do So instead of using V BB in calculations, you would just use V CC instead. V CE= V CC - I C x R C= 15v - (7.68mA x 1KΩ)= 7.32vīase bias can also be done with a single supply voltage, V CC, with V BB omitted. With I C then known, the collector-emitter voltage, V CE can be calculated. The collector current I C can be calculated next: Since the voltage drop across a silicon junction is 0.7V, the value of V BE=0.7V. The base current can be found by dividing the voltage across resistor R B by the value of The first calculation we will make is for the base current I B. Or else, it's impossible to tell whether the voltage and current values are correct or not. When using any biasing technique, calculations must be made of the various voltages and currents through a BJT So the total output current, I C will be I C=β dc x I B. β dc is the amplification factor by which the base current getsĪmplified by. Using the base biasing method, the collector current I C is dependent only on the values of The collector resistor, R C provides the desired voltage in the collector circuit.

This voltage, reverse-biases the transistor, so that the transistor has sufficient power to have an amplified outputĬollector current. V CC is the collector supply voltage, which is required for a transistor to have sufficient power R B is a resistance value that is used to provide the desired value of base current Iī. V BB is the base supply voltage, which is used to give the transistor sufficient current to V BB, is the correct voltage, which then supplies the correct current so that the BJT has enough base current toīelow is a typical BJT receiving base bias: Base bias ensures that the voltage fed to the base, Therefore, it's very important that a transistor is biased correctly for it to produceīase bias the simplest way to bias a BJT transistor. Produce clipping of the signal or produce too low of gain.
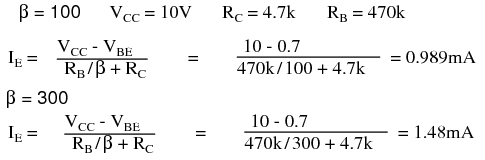
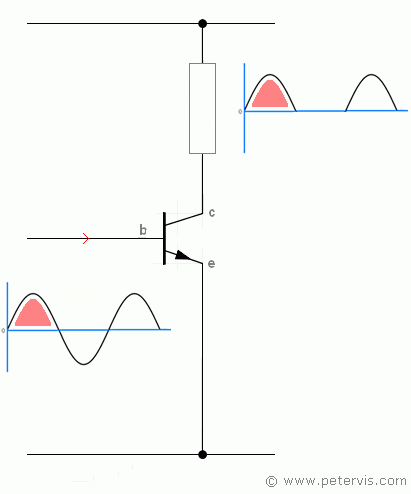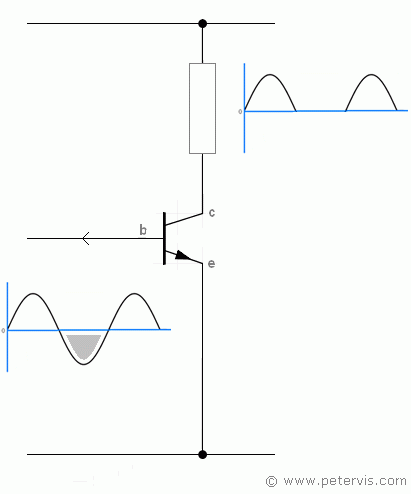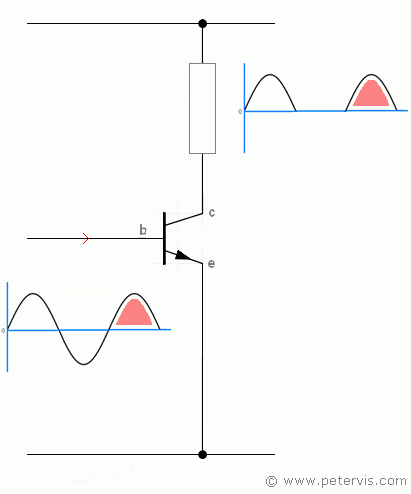
Without appropriate transistor biasing, the transistor may not function at all or amplify very poorly, such as


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
